CD Calculator
Calculate the interest earned on a fixed-rate certificate of deposit (CD) when it reaches maturity at the end of its term.
Results:
| Total Value: | $12,461.82
|
| Interest Earned: | $2,461.82
|
Balance by Year
On this page:
How to Calculate CD Interest
A certificate of deposit, or CD, is a savings product sold by banks and credit unions. CDs are called share certificates when sold by credit unions but are otherwise identical.
In exchange for leaving the principal amount in the financial institution for the term of the CD, you receive an interest rate on the principal that is typically higher than you would get in an ordinary savings account. CDs and other savings products are federally insured by either the FDIC or the NCUA (depending on where you buy them) up to a $250,000 limit.
You can usually find information about current CD rates on a financial institution’s website. CD rates are usually expressed in two ways:
- As a basic interest or dividend rate (depending on whether it is a bank or a credit union)
- As an APY rate, which will usually be slightly higher
What’s the Difference Between the Dividend Rate and APY?
The interest or dividend rate does not include any compounding of the CD’s interest, while the APY includes the effect of compounding interest. With compound interest, interest is accrued on prior interest accrued and the principal balance.
The effect of compounding interest provides you with a higher return on your CD, which means that the APY rate represents your actual rate of return. Most CDs provide compound interest on either a daily or monthly basis.
A CD that compounds more frequently (such as daily vs. monthly) will result in more interest being earned by that CD.
How to Use the CD Calculator to Calculate Interest
To calculate a CD’s interest, you can simply enter the relevant information into the handy calculator above:
- The initial deposit amount in dollars
- The term to maturity, in months or years
- The APY interest rate (which includes any compounding)
If you’d like to do the math yourself, you can use the compound interest formula for a CD.
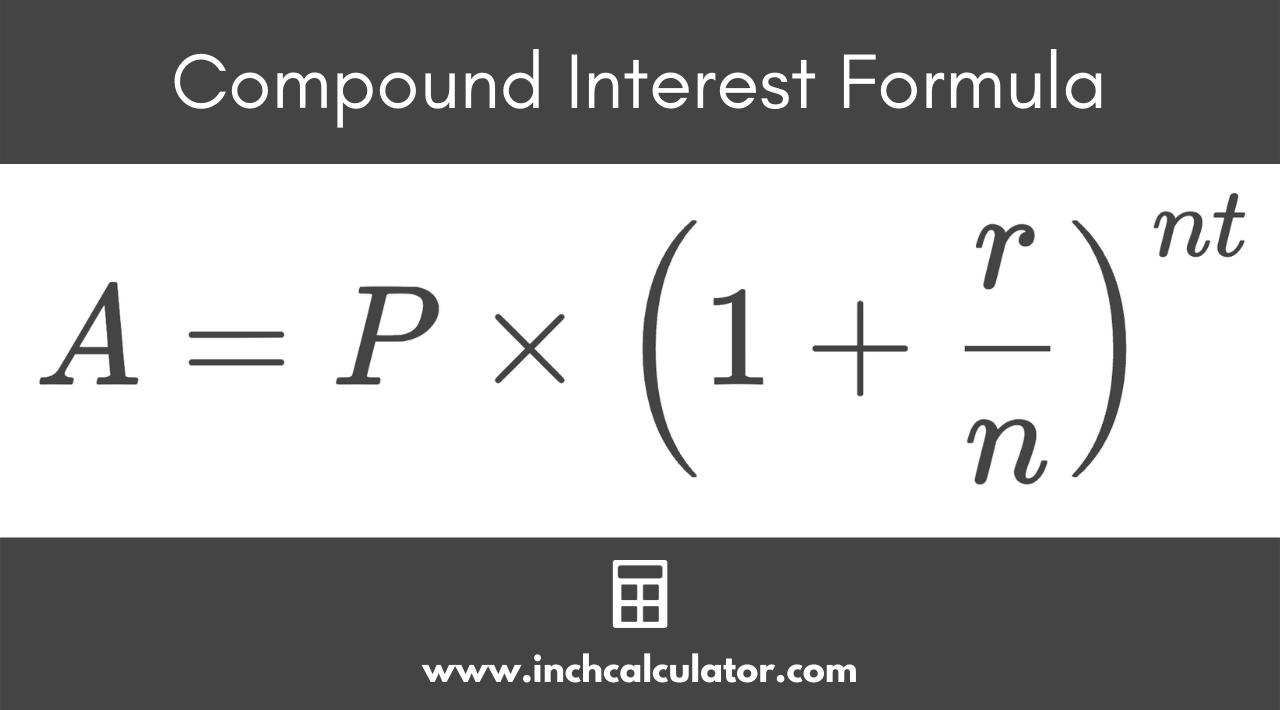
CD Compound Interest Formula
The compound interest rate formula is as follows:
Where:
A = future value
P = present value (initial deposit)
r = interest rate (basic rate, not APY)
n = number of times interest is compounded per year
t = CD term in years
For example, let’s say you are going to buy a $20,000 CD at 4% interest for a term of 5 years, with the interest compounded daily. How much in total interest will you receive?
Let’s use the compound interest formula above. (we also have a daily compound interest calculator for this). Since interest is compounded daily, n will equal 365 (the number of days in a year), and t will equal 5 (the number of years in the term).
Thus, the total interest that you would receive on your $20,000 CD in this example is $4,428.
A Brief History of CDs
The first financial product that was similar in concept to a modern CD came into use by banks in Europe during the 1600s. Depositors whose funds were then lent out by a bank were paid interest for a specific period of time.
This was done so that depositors would keep their funds in the bank and not withdraw them. This is generally how contemporary CDs work for today’s consumers.
In the US, CDs were introduced in the early 1800s. In those days, before the electronic banking system came into use, buyers would receive an actual certificate so that the bankers and the depositors could keep track of the CDs that had been issued. Unfortunately, if the bank were to fail, the depositors could lose their money.
The next major advance for bank customers was the creation of the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) after the crash of the stock market in 1929. The FDIC regulates banks and protects the assets of depositors with FDIC insurance.
Today, CDs are available at both banks and credit unions (where they are called Share Certificates). Share Certificates purchased at credit unions are likewise insured, but by the NCUA (National Credit Union Administration).
CD Ladders
CD ladders are a structured savings strategy that you create composed of multiple CDs that mature on a staggered basis. As each CD matures, you roll it over into another CD with either the same or a different maturity date.
A CD ladder is designed to provide a higher yet fully-insured rate of return that also meets your personal liquidity needs, whether that is every few months, annually, or even longer-term.
You can calculate your returns using a CD ladder with our CD ladder calculator
Frequently Asked Questions
What are CDs?
A Certificate of Deposit, or CD, is a savings product sold by banks and credit unions (who call them Share Certificates). In exchange for leaving the principal amount in the financial institution for the term of the CD, you receive an interest rate that is typically higher than what you would get in an ordinary savings account.
Can I get CDs at a credit union?
Yes. CDs purchased from a credit union are called Share Certificates. They are identical to CDs acquired from a bank.
Are CDs insured?
Yes, CDs and other savings products are insured up to a maximum of $250,000 per depositor by both the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) for bank accounts and the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) for credit union accounts.
What does principal mean for a CD?
The principal amount is what you pay for the CD when you purchase it. For example, a $1,000 CD will cost you $1,000 to buy. It can also be called the Initial Deposit.
What does term mean for a CD?
The term is the amount of time that a CD takes to mature. For example, a 6-month CD will take 6 months to mature. CD terms typically range from three months to 5 years.
What does interest mean for a CD?
The interest rate is the percentage of the principal amount that the financial institution will pay you for leaving your money in a CD until it matures.
What does APY mean for a CD?
The APY is the interest rate that you receive after the effects of compounded interest. It is higher than the basic interest rate.
What is compounded interest?
Compounded interest is paid at regular intervals during the term of your CD. For example, if your interest on a 6-month CD is compounded monthly, this means that at the end of each month, that month’s interest is added to your account, and then becomes part of the principal that each following month’s interest is calculated on.
This gives the effect of a higher interest rate because you are receiving interest on both the principal and your previous interest, with that amount increasing during each specified compounding interval during the term of the CD.
What happens if I need the money I put into a CD before it matures?
Withdrawing the funds used to purchase your CD before the term is complete will subject you to an early withdrawal penalty. The longer the CD term, the larger the penalty. While there are no-penalty CDs available, their rates tend to be lower than those of conventional CDs.
Is the interest on a CD taxable?
Unless your CD is housed within a tax-deferred or tax-exempt IRA account, the interest that you receive from it will be considered taxable income. Consult your tax adviser for more details.



