Kilowatts (kW) to Amps Conversion Calculator
Results: Current
| amps: | |
| milliamps: |
On this page:
- kW to Amps Calculator
- How to Convert Kilowatts to Amps
- kW to Amps Formula
- How to Account for Motor Efficiency and Power Factor
- How to Find Current for a Single-Phase AC Circuit
- How to Find the Current of a Three-Phase AC Circuit
- Motor Current Ratings (Three-Phase AC)
- Motor Current Ratings (Single-Phase AC)
- References
How to Convert Kilowatts to Amps
It is possible to convert kilowatts (kW) to amps using the Watt’s Law power formula. The power formula states that current = power ÷ voltage.
To adapt the power formula to using kilowatts, first start by converting kilowatts to watts, which can be done by multiplying the power in kilowatts by 1,000 to get the number of watts.
Then, apply the power formula by dividing the power (in watts) by the voltage (in volts) to find the current (in amps).
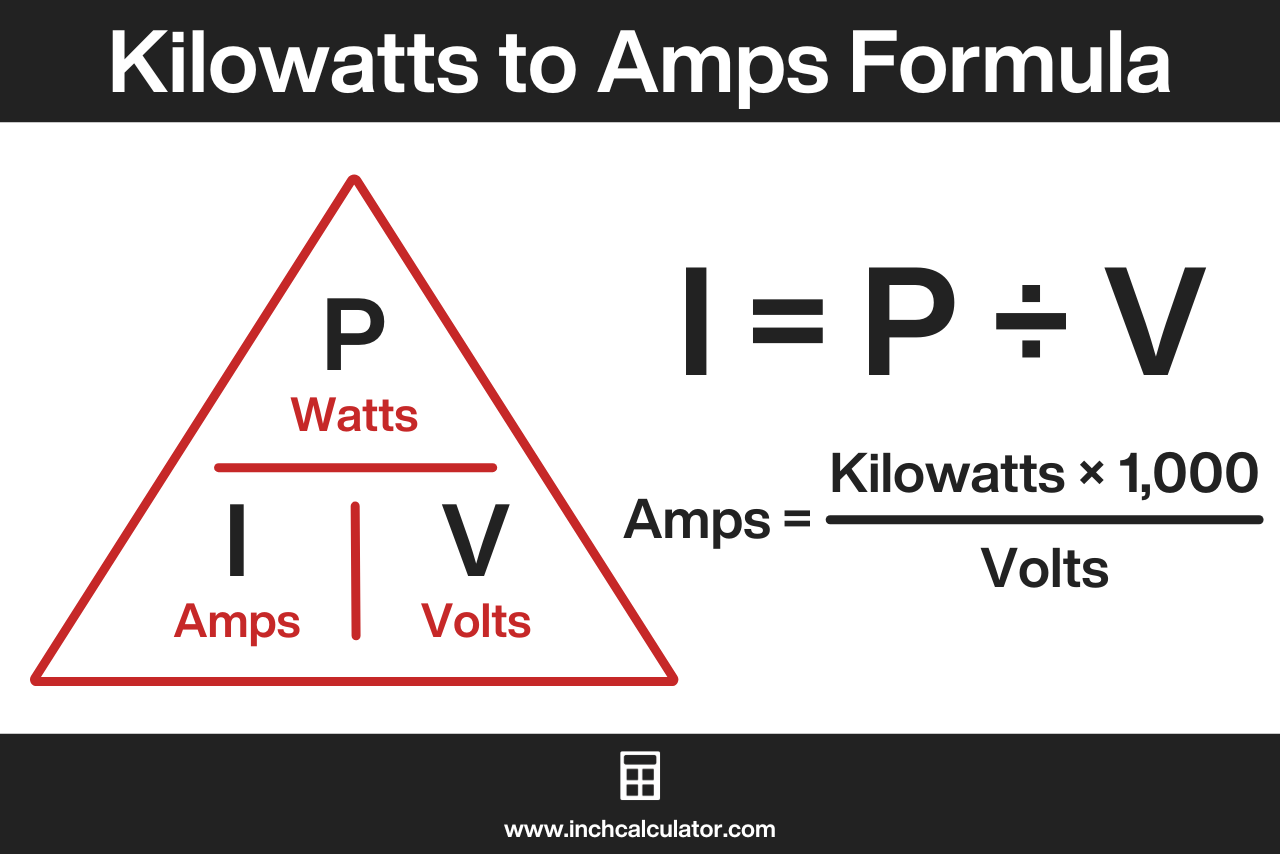
kW to Amps Formula
Thus, for DC and single-phase AC circuits, the formula to convert kilowatts to amps is:[1]
I(A) = P(kW) × 1,000 / V(V)
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in kilowatts multiplied by 1,000 (to convert to watts), divided by the voltage V in volts.
For example, let’s find the current of a circuit with 1 kW of power at 120 volts.
I(A) = 1 kW × 1,000 / 120 V
I(A) = 1,000 W / 120 V
I(A) = 8.33 A
So, generating 1 kW of power at 120 volts will draw 8.33 amps of current.
How to Account for Motor Efficiency and Power Factor
Equipment is often not 100% efficient with power usage, and this must be factored in to find the number of amps consumed for a given output power. Efficiency of the motor η, is defined as the ratio of power output to power input.
To find the input current required to achieve a certain motor output power, use the following equation.
I(A) = P(kW) × 1,000 / V(V) × η
Thus, the current I in amps is equal to the power P in kilowatts multiplied by 1,000, divided by the product of the voltage V in volts and the efficiency η.
How to Find Current for a Single-Phase AC Circuit
The magnitude of real and reactive power together in AC circuits is called the apparent power, and the power factor is the ratio of real power to apparent power.[2]
To find the input current required to achieve a certain output power in a single-phase AC circuit accounting for power factor and efficiency, use the following equation.[1]
I(A) = P(kW) × 1,000 / V(V) × η × PF
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in kilowatts multiplied by 1,000, divided by the product of the voltage V in volts, the efficiency η, and the power factor PF. Try our power factor calculator to get the power factor if needed.
For example, let’s find the current of a 5 kW motor with an efficiency of 75% and a power factor of 0.8 at 240 volts.
I(A) = 5 kW × 1,000 / 240 V × 0.75 × 0.8
I(A) = 5,000 W / 144 V
I(A) = 34.72 A
In this example, the 5 kW motor will draw 34.72 amps of current.
How to Find the Current of a Three-Phase AC Circuit
The formula to convert kilowatts to amps for a three-phase AC circuit is slightly different from the formula for a single-phase circuit. Use one of the formulas below for line to line or line to neutral RMS voltages.[1][3]
Using Line-to-Line Voltage
I(A) = P(kW) × 1,000 / VL-L(V) × η × PF × √3
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in kilowatts multiplied by 1,000, divided by the product of the line-to-line voltage V in volts, the efficiency η, the power factor PF, and the square root of 3.
This formula measures the current draw for one pair of wires in the three-phase system; to calculate the current for all three pairs of wires, you need to multiply the result by three.
Using Line to Neutral Voltage
I(A) = P(kW) × 1,000 / VL-N(V) × η × PF × 3
The current I in amps is equal to the power P in kilowatts multiplied by 1,000, divided by 3 times the product of the line-to-neutral voltage V in volts, the efficiency η, and the power factor PF.
This formula measures the current draw for all three wires in the three-phase system; to calculate the current for a single wire, you need to divide the result by three.
For example, find the current usage of a 25 kW three-phase motor with an efficiency of 80% and a power factor of 1 at 240 volts (line to line).
I(A) = 25 kW × 1,000 / 240 V × 0.8 × 1 × √3
I(A) = 25,000 W / 332.55 V
I(A) = 75.18 A
To convert watts to amps, use our watts to amps conversion calculator.
Motor Current Ratings (Three-Phase AC)
| Power | Current at 120V | Current at 208V | Current at 240V | Current at 277V | Current at 480V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 kW | 6.014 A | 3.47 A | 3.007 A | 2.605 A | 1.504 A |
| 2 kW | 12.028 A | 6.939 A | 6.014 A | 5.211 A | 3.007 A |
| 3 kW | 18.042 A | 10.409 A | 9.021 A | 7.816 A | 4.511 A |
| 4 kW | 24.056 A | 13.879 A | 12.028 A | 10.421 A | 6.014 A |
| 5 kW | 30.07 A | 17.348 A | 15.035 A | 13.027 A | 7.518 A |
| 6 kW | 36.084 A | 20.818 A | 18.042 A | 15.632 A | 9.021 A |
| 7 kW | 42.098 A | 24.288 A | 21.049 A | 18.238 A | 10.525 A |
| 8 kW | 48.113 A | 27.757 A | 24.056 A | 20.843 A | 12.028 A |
| 9 kW | 54.127 A | 31.227 A | 27.063 A | 23.448 A | 13.532 A |
| 10 kW | 60.141 A | 34.697 A | 30.07 A | 26.054 A | 15.035 A |
| 15 kW | 90.211 A | 52.045 A | 45.105 A | 39.081 A | 22.553 A |
| 20 kW | 120.28 A | 69.393 A | 60.141 A | 52.107 A | 30.07 A |
| 25 kW | 150.35 A | 86.741 A | 75.176 A | 65.134 A | 37.588 A |
| 30 kW | 180.42 A | 104.09 A | 90.211 A | 78.161 A | 45.105 A |
| 35 kW | 210.49 A | 121.44 A | 105.25 A | 91.188 A | 52.623 A |
| 40 kW | 240.56 A | 138.79 A | 120.28 A | 104.21 A | 60.141 A |
| 45 kW | 270.63 A | 156.13 A | 135.32 A | 117.24 A | 67.658 A |
| 50 kW | 300.7 A | 173.48 A | 150.35 A | 130.27 A | 75.176 A |
| 55 kW | 330.77 A | 190.83 A | 165.39 A | 143.3 A | 82.693 A |
| 60 kW | 360.84 A | 208.18 A | 180.42 A | 156.32 A | 90.211 A |
| 65 kW | 390.91 A | 225.53 A | 195.46 A | 169.35 A | 97.729 A |
| 70 kW | 420.98 A | 242.88 A | 210.49 A | 182.38 A | 105.25 A |
| 75 kW | 451.05 A | 260.22 A | 225.53 A | 195.4 A | 112.76 A |
| 80 kW | 481.13 A | 277.57 A | 240.56 A | 208.43 A | 120.28 A |
| 85 kW | 511.2 A | 294.92 A | 255.6 A | 221.46 A | 127.8 A |
| 90 kW | 541.27 A | 312.27 A | 270.63 A | 234.48 A | 135.32 A |
| 95 kW | 571.34 A | 329.62 A | 285.67 A | 247.51 A | 142.83 A |
| 100 kW | 601.41 A | 346.97 A | 300.7 A | 260.54 A | 150.35 A |
| 125 kW | 751.76 A | 433.71 A | 375.88 A | 325.67 A | 187.94 A |
| 150 kW | 902.11 A | 520.45 A | 451.05 A | 390.81 A | 225.53 A |
| 175 kW | 1,052.5 A | 607.19 A | 526.23 A | 455.94 A | 263.12 A |
| 200 kW | 1,202.8 A | 693.93 A | 601.41 A | 521.07 A | 300.7 A |
| 225 kW | 1,353.2 A | 780.67 A | 676.58 A | 586.21 A | 338.29 A |
| 250 kW | 1,503.5 A | 867.41 A | 751.76 A | 651.34 A | 375.88 A |
| 275 kW | 1,653.9 A | 954.15 A | 826.93 A | 716.48 A | 413.47 A |
| 300 kW | 1,804.2 A | 1,040.9 A | 902.11 A | 781.61 A | 451.05 A |
| 325 kW | 1,954.6 A | 1,127.6 A | 977.29 A | 846.75 A | 488.64 A |
| 350 kW | 2,104.9 A | 1,214.4 A | 1,052.5 A | 911.88 A | 526.23 A |
| 375 kW | 2,255.3 A | 1,301.1 A | 1,127.6 A | 977.01 A | 563.82 A |
| 400 kW | 2,405.6 A | 1,387.9 A | 1,202.8 A | 1,042.1 A | 601.41 A |
| 425 kW | 2,556 A | 1,474.6 A | 1,278 A | 1,107.3 A | 638.99 A |
| 450 kW | 2,706.3 A | 1,561.3 A | 1,353.2 A | 1,172.4 A | 676.58 A |
| 475 kW | 2,856.7 A | 1,648.1 A | 1,428.3 A | 1,237.6 A | 714.17 A |
| 500 kW | 3,007 A | 1,734.8 A | 1,503.5 A | 1,302.7 A | 751.76 A |
| 525 kW | 3,157.4 A | 1,821.6 A | 1,578.7 A | 1,367.8 A | 789.35 A |
| 550 kW | 3,307.7 A | 1,908.3 A | 1,653.9 A | 1,433 A | 826.93 A |
| 575 kW | 3,458.1 A | 1,995.1 A | 1,729 A | 1,498.1 A | 864.52 A |
| 600 kW | 3,608.4 A | 2,081.8 A | 1,804.2 A | 1,563.2 A | 902.11 A |
| 625 kW | 3,758.8 A | 2,168.5 A | 1,879.4 A | 1,628.4 A | 939.7 A |
| 650 kW | 3,909.1 A | 2,255.3 A | 1,954.6 A | 1,693.5 A | 977.29 A |
| 675 kW | 4,059.5 A | 2,342 A | 2,029.7 A | 1,758.6 A | 1,014.9 A |
| 700 kW | 4,209.8 A | 2,428.8 A | 2,104.9 A | 1,823.8 A | 1,052.5 A |
| 725 kW | 4,360.2 A | 2,515.5 A | 2,180.1 A | 1,888.9 A | 1,090 A |
| 750 kW | 4,510.5 A | 2,602.2 A | 2,255.3 A | 1,954 A | 1,127.6 A |
| 775 kW | 4,660.9 A | 2,689 A | 2,330.5 A | 2,019.2 A | 1,165.2 A |
| 800 kW | 4,811.3 A | 2,775.7 A | 2,405.6 A | 2,084.3 A | 1,202.8 A |
| 825 kW | 4,961.6 A | 2,862.5 A | 2,480.8 A | 2,149.4 A | 1,240.4 A |
| 850 kW | 5,112 A | 2,949.2 A | 2,556 A | 2,214.6 A | 1,278 A |
| 875 kW | 5,262.3 A | 3,035.9 A | 2,631.2 A | 2,279.7 A | 1,315.6 A |
| 900 kW | 5,412.7 A | 3,122.7 A | 2,706.3 A | 2,344.8 A | 1,353.2 A |
| 925 kW | 5,563 A | 3,209.4 A | 2,781.5 A | 2,410 A | 1,390.8 A |
| 950 kW | 5,713.4 A | 3,296.2 A | 2,856.7 A | 2,475.1 A | 1,428.3 A |
| 975 kW | 5,863.7 A | 3,382.9 A | 2,931.9 A | 2,540.2 A | 1,465.9 A |
| 1000 kW | 6,014.1 A | 3,469.7 A | 3,007 A | 2,605.4 A | 1,503.5 A |
Motor Current Ratings (Single-Phase AC)
| Power | Current at 120V | Current at 240V |
|---|---|---|
| 1 kW | 10.417 A | 5.208 A |
| 2 kW | 20.833 A | 10.417 A |
| 3 kW | 31.25 A | 15.625 A |
| 4 kW | 41.667 A | 20.833 A |
| 5 kW | 52.083 A | 26.042 A |
| 6 kW | 62.5 A | 31.25 A |
| 7 kW | 72.917 A | 36.458 A |
| 8 kW | 83.333 A | 41.667 A |
| 9 kW | 93.75 A | 46.875 A |
| 10 kW | 104.17 A | 52.083 A |
| 15 kW | 156.25 A | 78.125 A |
| 20 kW | 208.33 A | 104.17 A |
| 25 kW | 260.42 A | 130.21 A |
| 30 kW | 312.5 A | 156.25 A |
| 35 kW | 364.58 A | 182.29 A |
| 40 kW | 416.67 A | 208.33 A |
| 45 kW | 468.75 A | 234.38 A |
| 50 kW | 520.83 A | 260.42 A |
| 55 kW | 572.92 A | 286.46 A |
| 60 kW | 625 A | 312.5 A |
| 65 kW | 677.08 A | 338.54 A |
| 70 kW | 729.17 A | 364.58 A |
| 75 kW | 781.25 A | 390.63 A |
| 80 kW | 833.33 A | 416.67 A |
| 85 kW | 885.42 A | 442.71 A |
| 90 kW | 937.5 A | 468.75 A |
| 95 kW | 989.58 A | 494.79 A |
| 100 kW | 1,041.7 A | 520.83 A |
| 125 kW | 1,302.1 A | 651.04 A |
| 150 kW | 1,562.5 A | 781.25 A |
| 175 kW | 1,822.9 A | 911.46 A |
| 200 kW | 2,083.3 A | 1,041.7 A |
| 225 kW | 2,343.8 A | 1,171.9 A |
| 250 kW | 2,604.2 A | 1,302.1 A |
| 275 kW | 2,864.6 A | 1,432.3 A |
| 300 kW | 3,125 A | 1,562.5 A |
| 325 kW | 3,385.4 A | 1,692.7 A |
| 350 kW | 3,645.8 A | 1,822.9 A |
| 375 kW | 3,906.3 A | 1,953.1 A |
| 400 kW | 4,166.7 A | 2,083.3 A |
| 425 kW | 4,427.1 A | 2,213.5 A |
| 450 kW | 4,687.5 A | 2,343.8 A |
| 475 kW | 4,947.9 A | 2,474 A |
| 500 kW | 5,208.3 A | 2,604.2 A |
| 525 kW | 5,468.8 A | 2,734.4 A |
| 550 kW | 5,729.2 A | 2,864.6 A |
| 575 kW | 5,989.6 A | 2,994.8 A |
| 600 kW | 6,250 A | 3,125 A |
| 625 kW | 6,510.4 A | 3,255.2 A |
| 650 kW | 6,770.8 A | 3,385.4 A |
| 675 kW | 7,031.3 A | 3,515.6 A |
| 700 kW | 7,291.7 A | 3,645.8 A |
| 725 kW | 7,552.1 A | 3,776 A |
| 750 kW | 7,812.5 A | 3,906.3 A |
| 775 kW | 8,072.9 A | 4,036.5 A |
| 800 kW | 8,333.3 A | 4,166.7 A |
| 825 kW | 8,593.8 A | 4,296.9 A |
| 850 kW | 8,854.2 A | 4,427.1 A |
| 875 kW | 9,114.6 A | 4,557.3 A |
| 900 kW | 9,375 A | 4,687.5 A |
| 925 kW | 9,635.4 A | 4,817.7 A |
| 950 kW | 9,895.8 A | 4,947.9 A |
| 975 kW | 10,156 A | 5,078.1 A |
| 1000 kW | 10,417 A | 5,208.3 A |
References
- Miller, C., NFPA's Electrical References, National Fire Protection Association, 2004, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 67-75. https://www.google.com/books/edition/NFPA_s_Electrical_References/raUyIi7i-asC
- Fiore, J., AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach, 2022, 274. http://www.dissidents.com/resources/ACElectricalCircuitAnalysis.pdf
- Miller, C., Ugly’s Electrical References, 2020 Edition, 2020, Jones & Bartlett Learning, 16-23. https://books.google.com/books?id=1kS8DwAAQBAJ



