Mean Absolute Deviation Calculator – Find MAD
Find the mean absolute deviation of a data set by entering the numbers below.
Mean Absolute Deviation:
| MAD: | |
|---|---|
| Mean (x̄): | |
| Count (n): |
Steps to Solve
Apply the Mean Absolute Deviation Formula
Step One: Find the Mean
Step Two: Find the Absolute Value of the Difference (Δ) Between Each Number and the Mean
Step Three: Find the MAD
On this page:
How to Find the Mean Absolute Deviation
In statistics, the mean absolute deviation, or MAD, is the average difference between each value in the set and the set’s mean.
Like standard deviation, mean absolute deviation is a measure of the variability or dispersion in a data set. While standard deviation is the square root of the sum of squares of the deviations from the mean, MAD is the mean of those deviations.
Mean Absolute Deviation Formula
You can calculate the mean absolute deviation using a simple formula:
Where:
xi = each number in the set
x̄ = the mean
n = size of the set
So, the mean absolute deviation MAD is equal to the sum of the differences between each number in the set xi and the mean x̄, divided by the size of the set n
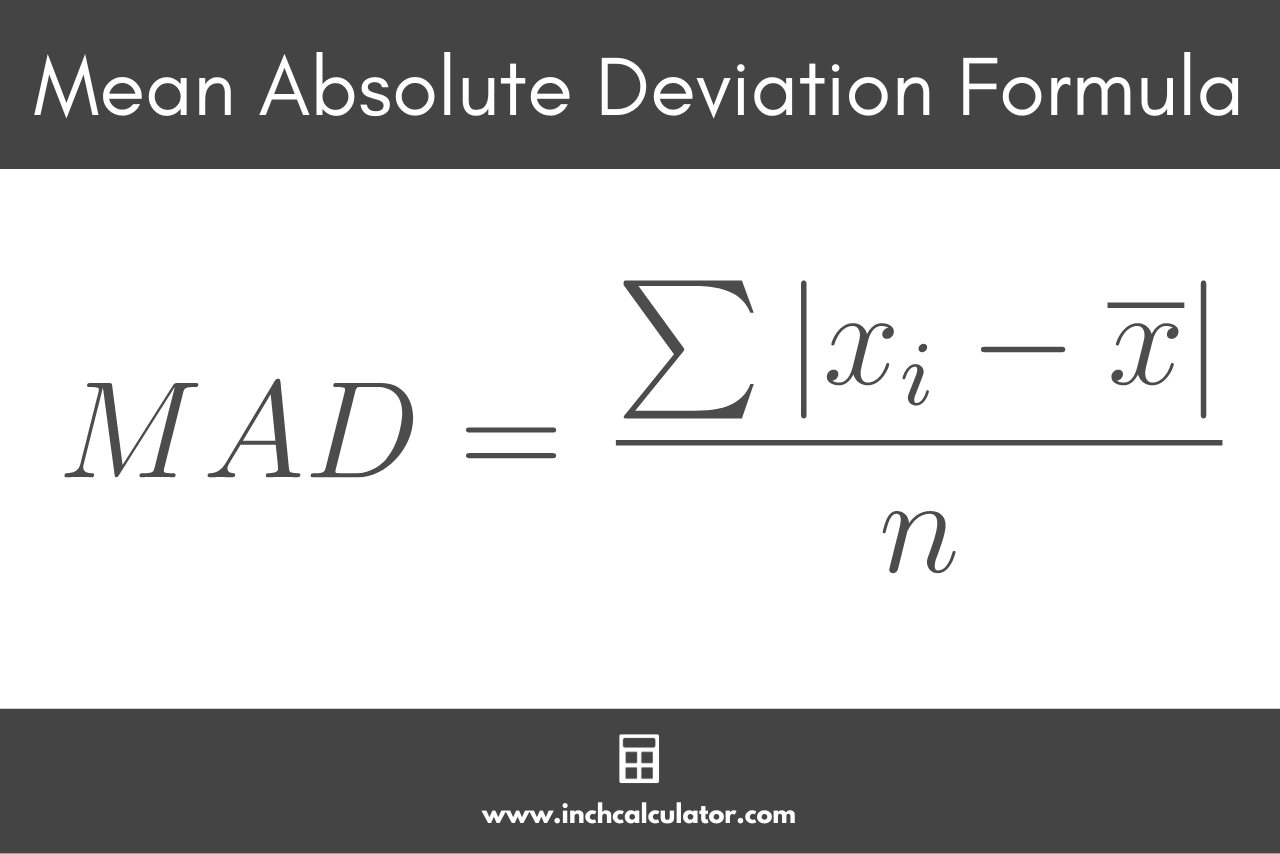
You can use the formula above to find the mean absolute deviation in a few easy steps.
Step One: Calculate the Mean
In order to use the formula above to calculate the MAD, you’ll first need to find the mean of the data. You can find the mean by adding each value in the set, and then dividing by the size of the set.
Step Two: Calculate the Difference Between Each Value and the Mean
Next, find the absolute value of the difference between each number and the mean. Subtract the mean from each number in the set and find the absolute value.
Step Three: Calculate the Mean Absolute Deviation
Finally, put it all together to find the mean absolute deviation. Sum up all of the differences together, then divide that by the number of elements in the set.
For example, let’s find the mean absolute deviation for the numbers [2,7,15,22]
Let’s start by finding the mean.
Next, let’s find the absolute value of the difference between each number and the mean.
Then, sum the differences together.
Finally, divide by the number of values in the set, which is 4.
Thus, the mean absolute deviation of the set of numbers above is equal to 7.


