Polygon Calculator
Calculate any part of a polygon using the polygon calculator below.
Results: Polygon Properties
| Side (a): | 3
|
| Area (A): | 9
|
| Perimeter (P): | 12
|
| Circumradius (R): | 2.121
|
| Inradius (r): | 1.5
|
| Interior Angle (α): | 90°
|
| Exterior Angle (β): | 90°
|
On this page:
How to Calculate the Properties of a Polygon
A polygon is a two-dimensional shape made up of straight line segments.
A regular polygon is a symmetrical polygon where all of the sides are equal in length, and all angles have the same angle. Examples of regular polygons include equilateral triangles, squares, pentagons, hexagons, and octagons.
How to Calculate the Area of a Polygon
The area of a polygon largely depends on its size and shape. You can calculate the area using a formula. For a regular polygon with n sides of length a, the formula to find the area is:
The area A of a regular polygon is equal to the number of sides n times the length of the sides a squared, divided by 4 times the tangent of pi times the number of sides.
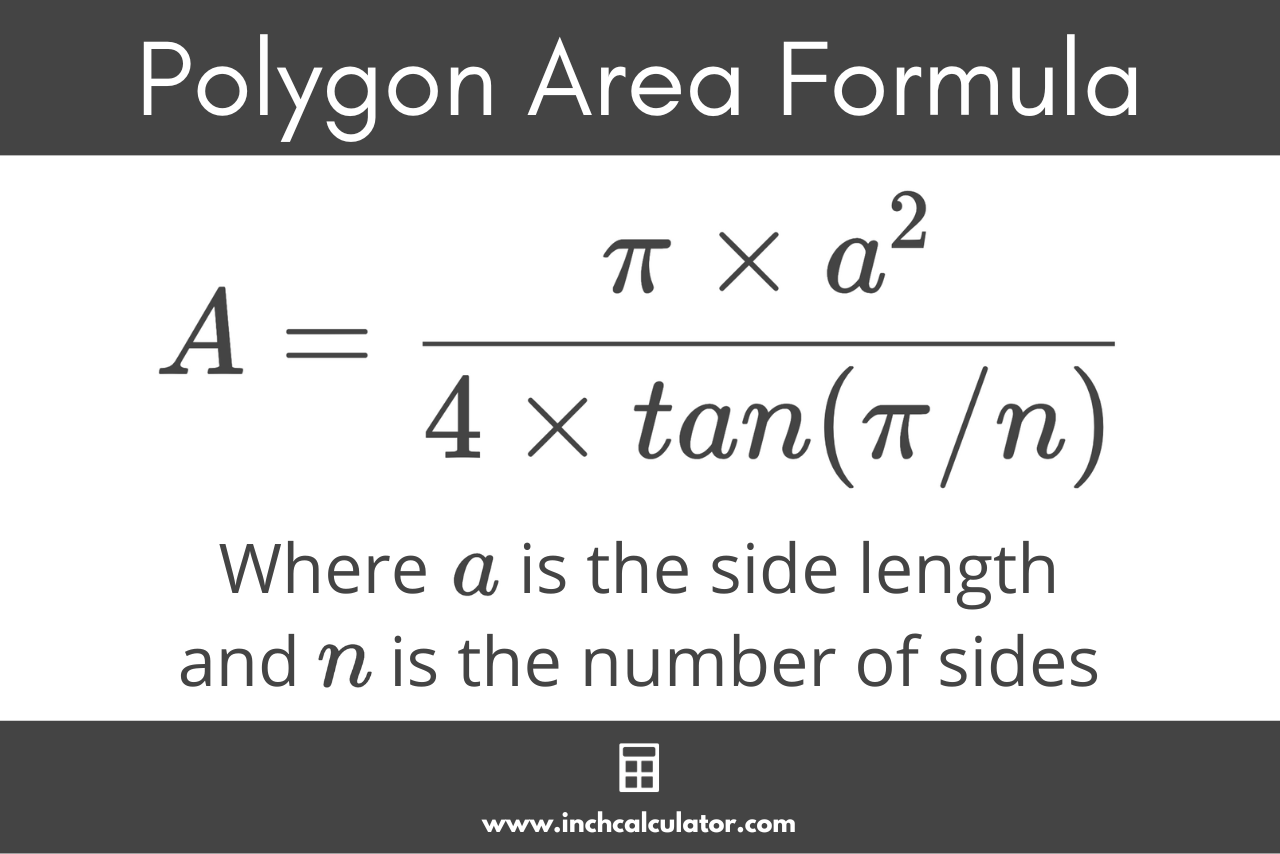
How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Polygon
The perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. You can calculate the perimeter of a regular polygon by multiplying the length of the sides by the number of sides.
How to Find the Angles of a Polygon
The interior angles of a polygon are the angles formed inside the polygon where two sides meet. Every polygon, whether regular or irregular, has interior angles that sum up to a certain value based on the number of sides it has.
For any polygon, the sum of its interior angles, taken one per vertex, always equals (n – 2) × 180°.
Therefore, the formula to calculate the interior angle α of a regular polygon is:
In contrast, the exterior angles of a polygon are the angles formed outside the polygon by extending one of its sides. For any polygon, the sum of its exterior angles, taken one per vertex, always equals 360°.
Therefore, the formula to calculate the exterior angle β of a regular polygon is simply 360 divided by the number of sides n:
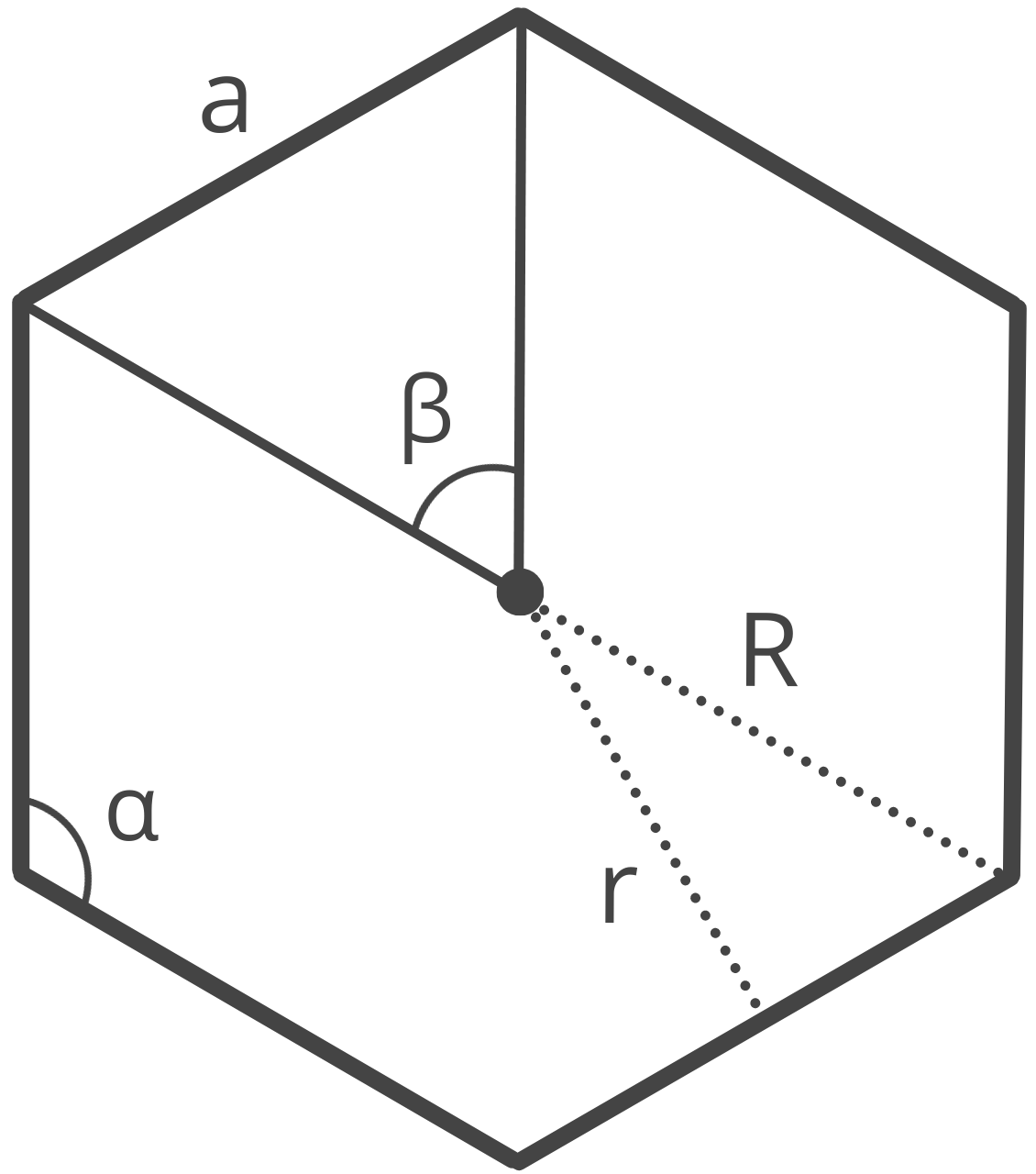
How to Find the Circumradius of a Polygon
The circumradius of a polygon is the radius of the circumscribed circle that passes through all of its vertices. You can calculate the circumradius R using the formula:
The circumradius R is equal to the length of the sides a divided by 2 times the sine of pi divided by the number of sides n.
How to Find the Inradius of a Polygon
The inradius, or the apothem, of a polygon is the radius of the inscribed circle that is entirely contained within the sides. The inradius is equal to the perpendicular distance from its center to one of its sides.
The formula to find the inradius r is:
The inradius r is equal to the length of the sides a divided by 2 times the tangent of pi divided by the number of sides n.


