Triangle Calculator
Use our triangle calculator to solve the angles and sides of a triangle using trigonometry. Enter three known values including at least one side to calculate the remaining properties of a triangle.
Results:
| side a = | 10
|
|---|---|
| side b = | 15
|
| side c = | 20
|
| angle α = |
28.955
0.50536
|
| angle β = |
46.5675
0.81276
|
| angle γ = |
104.478
1.8235
|
| area A = | 72.6184
|
| perimeter p = | 45
|
| semiperimeter s = | 22.5
|
| height ha = | 14.5237
|
| height hb = | 9.6825
|
| height hc = | 7.2618
|
| median ma = | 16.9558
|
| median mb = | 13.9194
|
| median mc = | 7.9057
|
| inradius r = | 3.2275
|
| circumradius R = | 10.328
|
Steps to Solve
Use the Law of Cosines to solve the angles α, β, γ:
Solve the perimeter p and semiperimeter s:
Use Heron's formula to find the area A:
Solve the height h of each side:
Solve the median m of each side:
Solve the inradius r and circumradius R:
On this page:
- Calculator
- How to Calculate a Triangle’s Missing Sides and Angles
- How to Use the Pythagorean Theorem
- How to Use the Law of Sines
- How to Use the Law of Cosines
- How to Calculate the Area of a Triangle
- How to Calculate the Height of a Triangle
- How to Calculate the Inradius and Circumradius
- Frequently Asked Questions
How to Calculate a Triangle’s Missing Sides and Angles
Triangles are polygons with three sides and three interior angles between them. There are several types of triangles, including isosceles, equilateral, scalene, obtuse, acute, and right triangles.
Using special rules such as the Pythagorean theorem, Law of Sines, and Law of Cosines, it’s possible to calculate any angle or side of a triangle if you know the length of at least one side and two remaining side lengths or angles.
How to Use the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle, the length of the hypotenuse squared is equal to the sum of the squares of each leg. For a right triangle with sides a and b, and a hypotenuse c, the Pythagorean theorem states:
a² + b² = c²
So, if you know the length of any two sides of a right triangle, you can calculate the length of the third side using this formula.
For example, let’s calculate the length of the hypotenuse for a right triangle having sides equal to 5 and 7.
5² + 7² = c²
25 + 49 = c²
74 = c²
√74 = c
8.6 = c
How to Use the Law of Sines
The Law of Sines or the Sine Rule states that for any oblique triangle (that is, a triangle that has sides not perpendicular to each other), the ratio of a side length to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. The Law of Sines states:
a / sin(α) = b / sin(β) = c / sin(γ)
Where:
a, b, and c are the lengths of the triangle’s sides
α, β, and γ are the angles opposite to sides a, b, and c.
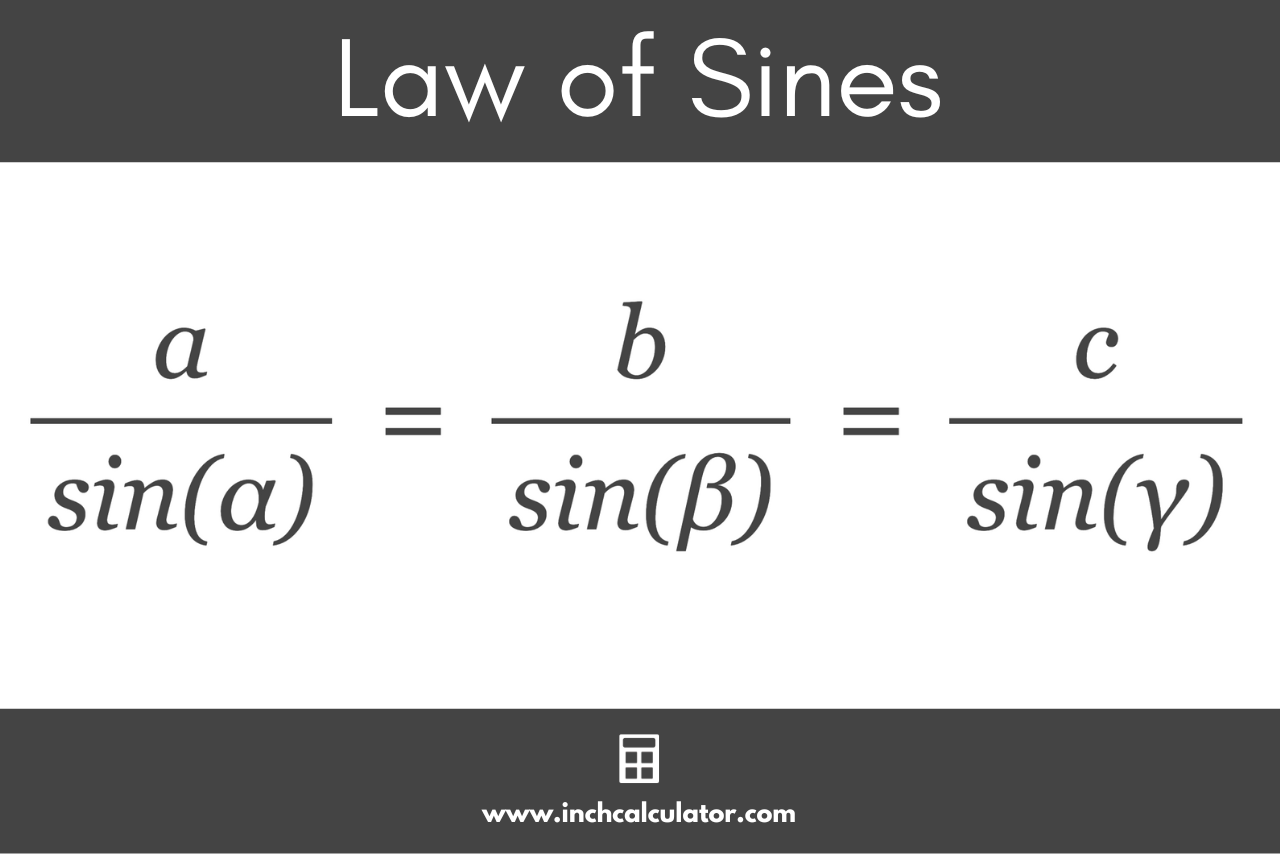
You can use this expression to calculate a side length or angle in a triangle if you know the opposite angle and another angle and side length.
For example, let’s calculate the length of side b for a triangle having an angle α equal to 45°, an angle β equal to 75°, and a side a equal to 10.
By substituting the known values into the Law of Sines expression and rearranging, you can solve for side b.
10 / sin(45°) = b / sin(75°)
b = 10 × sin(75°) / sin(45°)
b = 13.66
How to Use the Law of Cosines
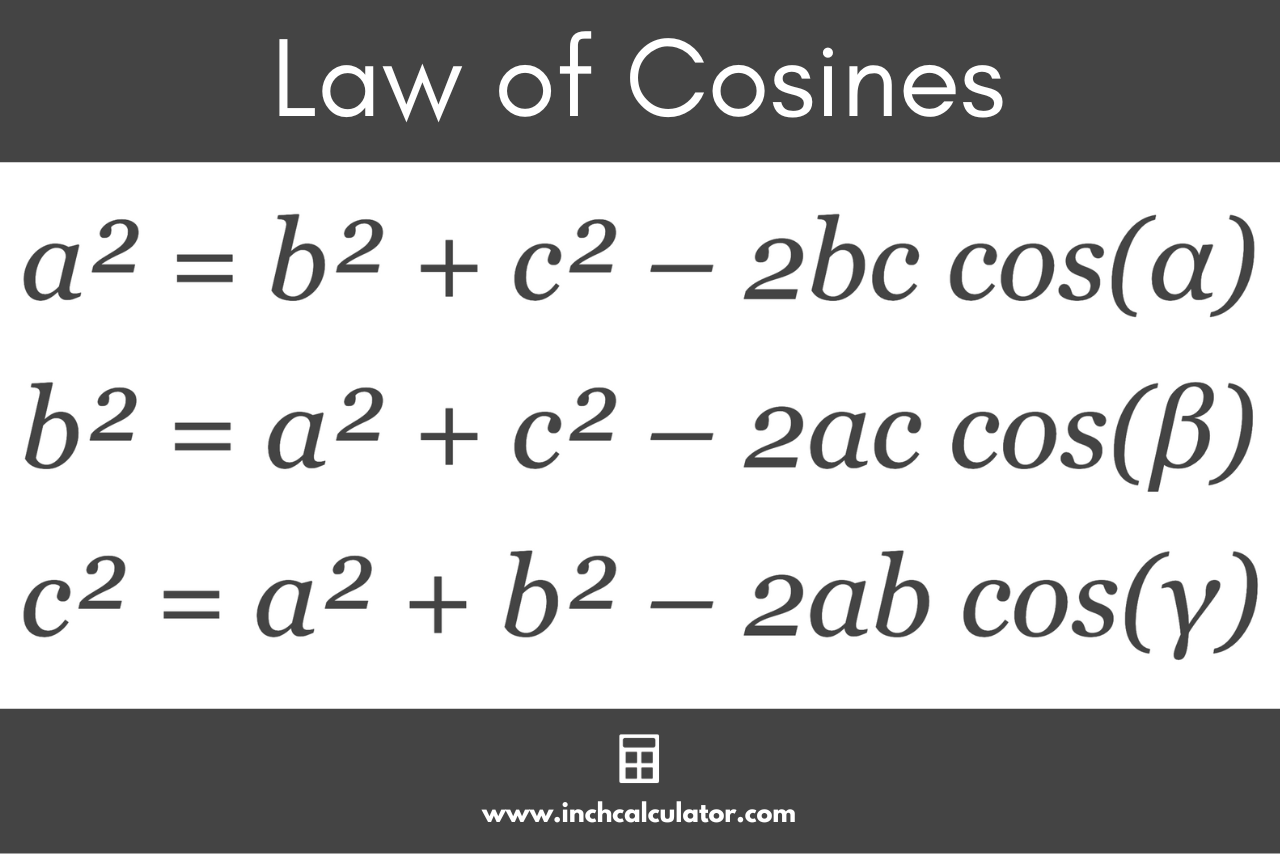
The Law of Cosines or Cosine Rule is a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem formula that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of its angles. The Law of Cosines states:
a² = b² + c² – 2bc cos(α)
b² = a² + c² – 2ac cos(β)
c² = a² + b² – 2ab cos(γ)
Where:
a, b, and c are the lengths of the triangle’s sides
α, β, and γ are the angles opposite to sides a, b, and c.
By substituting the known values into the Law of Cosines expression and rearranging, you can solve for any remaining side in a triangle.
For example, let’s calculate the length of side a for a triangle having an angle α equal to 45°, a side b equal to 10, and a side c equal to 14.
By substituting the known values into the Law of Cosines expression and rearranging, you can solve for side a.
a² = 10² + 14² – 2 × 10 × 14 cos(45°)
a² = 100 + 196 – 280 × 0.707
a² = 296 – 197.99
a² = 98.01
a = √98.01
a = 9.9
How to Calculate the Area of a Triangle
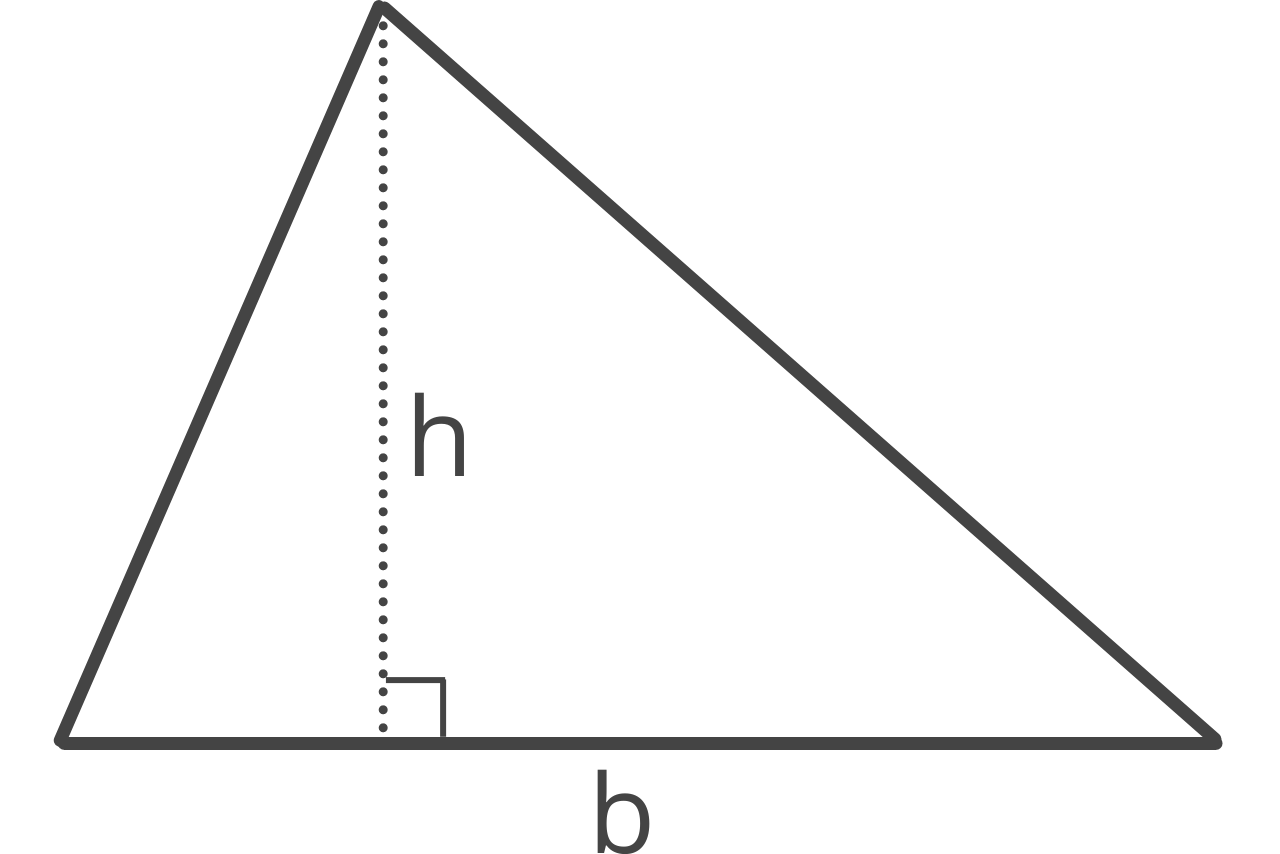
You can calculate the area of a triangle using several formulas. The base and height method is the most commonly used. The base and height area formula states:
A = 1 / 2bh
The triangle area A is equal to 1/2 times base b times height h.
You can also use the three-sides method (SSS or side-side-side), which is also known as Heron’s formula. Heron’s formula states:
s = a + b + c / 2
A = s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
How to Calculate the Height of a Triangle
You can calculate the height, or altitude, or a triangle using a simple formula using the length of the base and the area.
h = 2A / b
The height of a triangle h is equal to 2 times the area A divided by the length of base b.
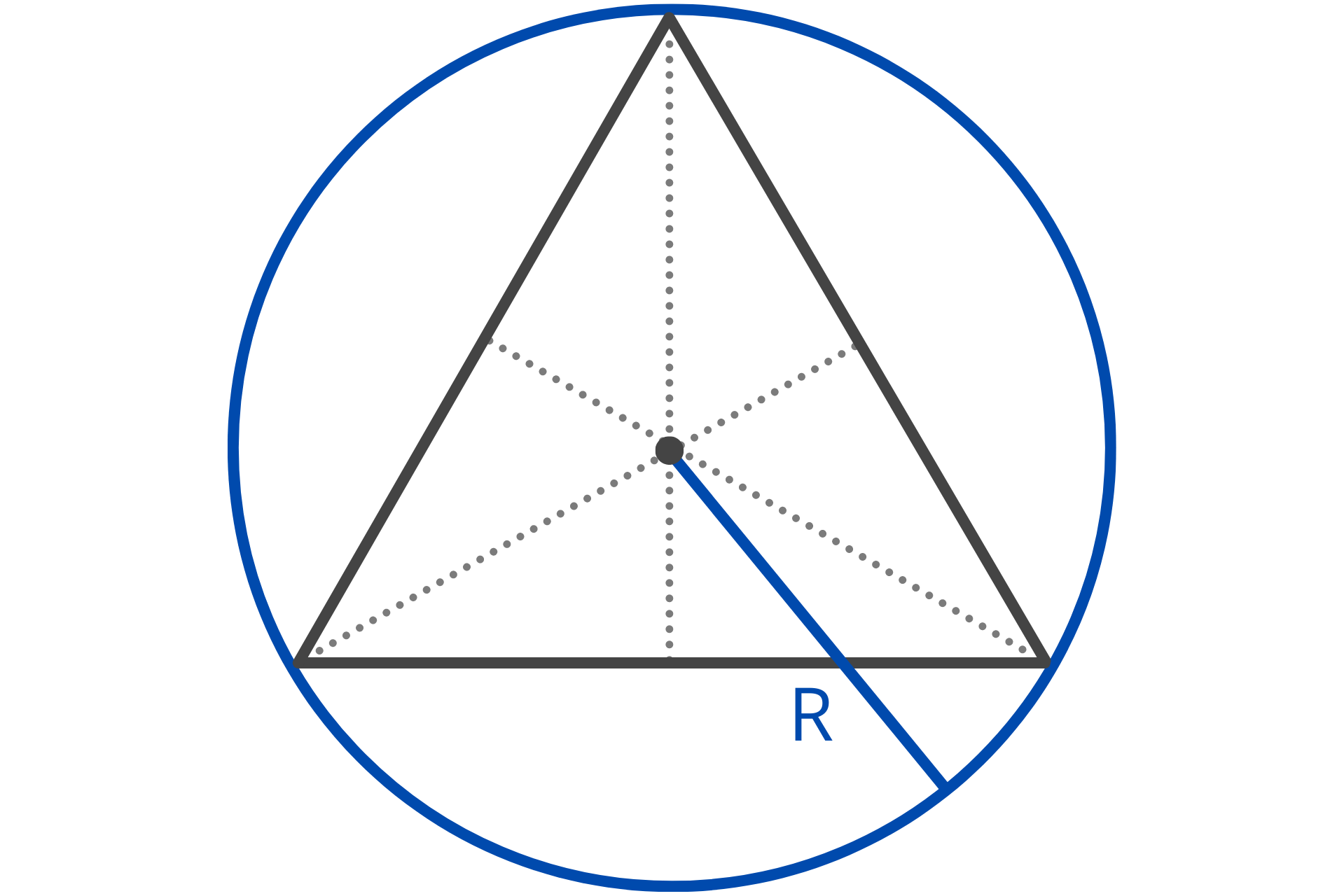
How to Calculate the Inradius and Circumradius
The inradius is the radius of the inscribed circle, which is a circle that is tangent to all three sides of the triangle. In other words, it is the largest circle that can fit inside the triangle.
You can use the following formula to calculate the inradius of a triangle.
r = A / s
The inradius r is equal to the area A divided by the semiperimeter s. The semiperimeter is equal to half the perimeter.
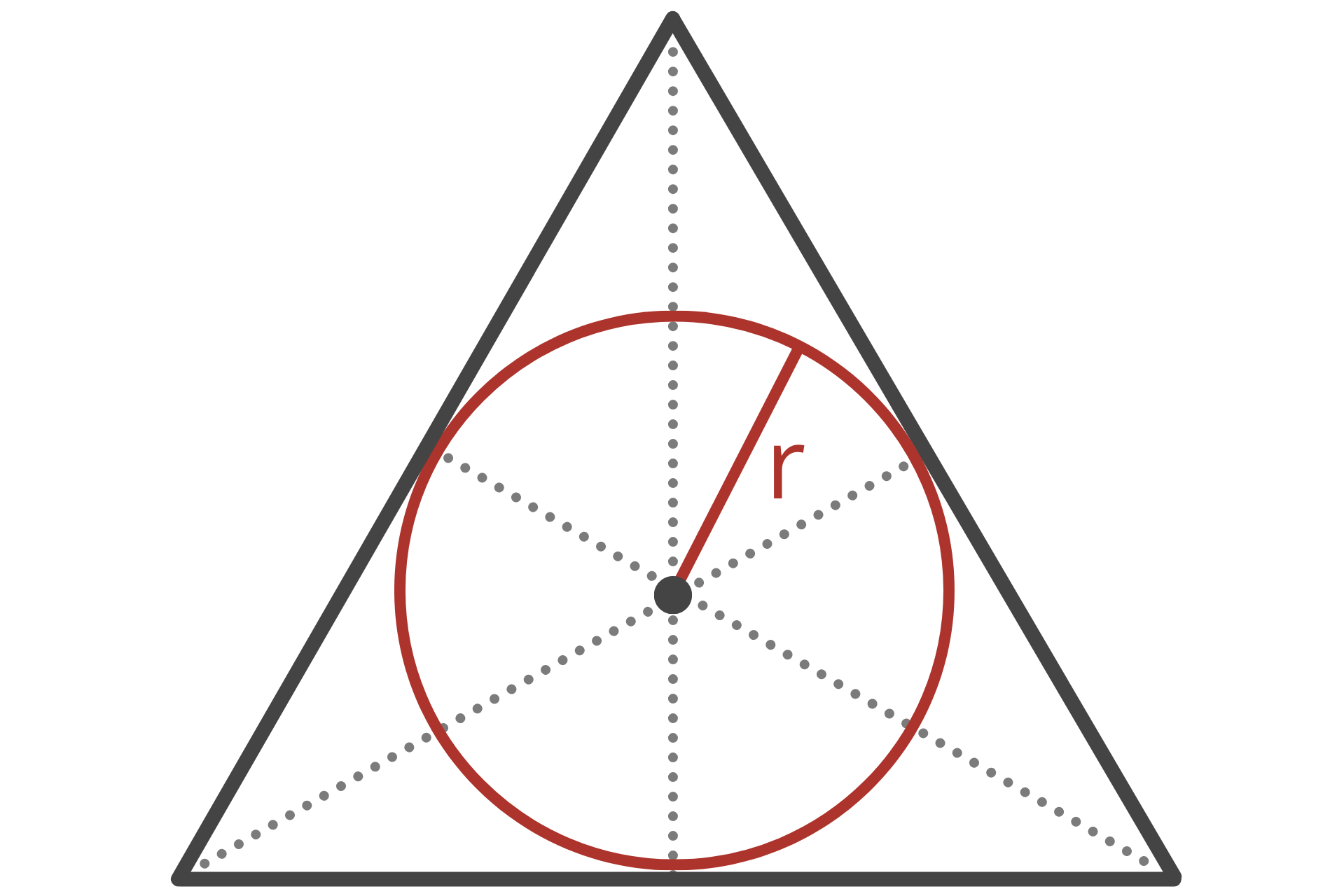
The circumradius is the radius of the circumscribed circle, which is the circle that passes through all three vertices of the triangle. In other words, it is the smallest circle that the triangle can fit inside of.
You can use the following formula to calculate the circumradius of a triangle.
R = a / 2sin(α)
The circumradius R is equal to the length of side a divided by 2 times the sine of the opposing angle α.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you solve for the third interior angle in a triangle?
If you know two of the three interior angles in any given triangle, you can easily calculate the third by subtracting the value of the two known angles from 180°. This is because, for any triangle, the total value of all the interior angles added together should always be equal to 180°.
How do you know if two triangles are congruent?
Two triangles are considered congruent if the corresponding sides of both triangles and their corresponding angles are equal.
How do you know if two triangles are similar?
Two triangles are considered similar if their corresponding angles are congruent (equal) and their corresponding sides are proportional. If the corresponding sides are also equal, then the triangle is considered congruent.


