Weighted Average Calculator
Enter the values in a data set and their respective weights to calculate the weighted average.
Weighted Average:
Steps to Find the Weighted Average
To find the weighted mean, use the following formula:
On this page:
How to Find a Weighted Average
A weighted average, sometimes called a weighted mean, is an average value that reflects the varying amount of importance of each value in a data set. This is different from the arithmetic mean, where each value contributes equally when calculating the average.
You can also think of the arithmetic mean as a special case of weighted means where the weights are all equal to 1.
Weighted averages are often used for applications such as sports statistics, class grades and GPA, job performance, credit scores, averaging the cost of capital (e.g. WACC), or calculating stock cost basis.
A classic example of weighted averages is school courses, where homework might be worth a smaller portion of the grade than the final exam.
They are also extensively used in survey sampling as a way to correct for over-participation by individuals from some backgrounds (e.g. the elderly) and under-participation by other groups (e.g. the young).
Weighted Average Formula
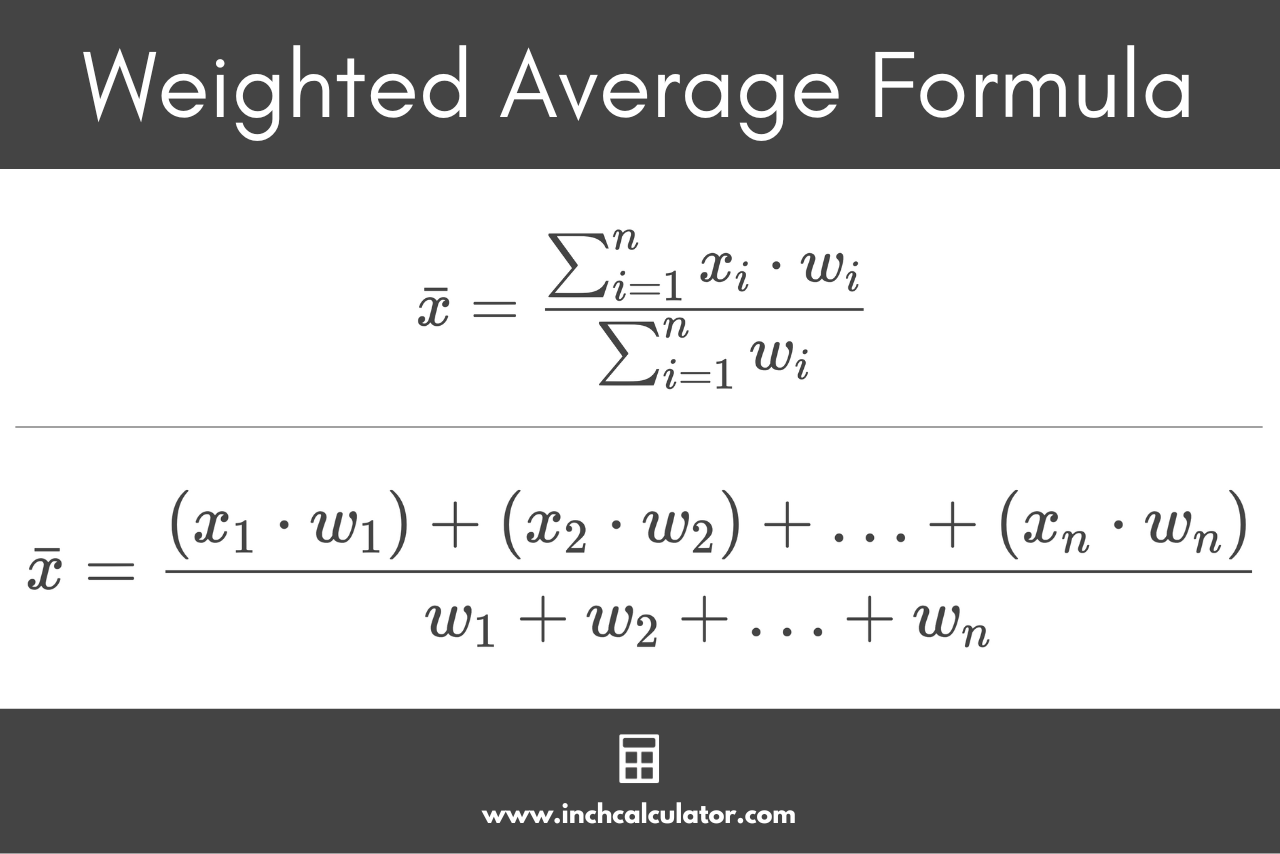
To calculate a weighted average or weighted mean, you can use the following formula:
This weighted average formula can be expressed more simply:
Thus, the weighted average x̄ is equal to the sum of the products of each weight and its value, divided by the sum of the weights.
For example, let’s use the weighted average formula to calculate a student’s grade average with the following courses and grades:
- class 1: 4 credits B (3.0)
- class 2: 3 credits A (4.0)
- class 3: 4 credits A- (3.7)
- class 4: 3 credits B+ (3.3)
This student’s GPA is 3.48.
This example should demystify how weighted averages work. You might also be interested in learning more about the geometric mean.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why would you use a weighted average instead of a mean?
A weighted average is used whenever observations should not have equal value in calculating the quantity of ultimate interest.
How do you know when to use a weighted average?
A weighted average is commonly used when there are repeated observations (e.g. multiple courses with the same letter grade) or when the quantity of interest calls for different weights (e.g. the syllabus assigns different weight to different assignments).


